Understanding how solar panels work – and what affects their performance – helps homeowners and businesses make informed decisions about solar energy.
How Solar Panels Generate Electricity
Solar panels generate electricity using photovoltaic (PV) cells, which convert sunlight into electricity. When sunlight hits a solar panel, it excites electrons within the PV cells. This movement of electrons creates a direct current (DC). An inverter then converts this DC electricity into alternating current (AC), which is the type of electricity used in homes, businesses and the National Grid.
Any electricity you don’t use immediately can either by exported to the grid for payment through the Smart Export Guarantee (SEG) or be stored in a solar battery use for evening or nighttime use.
Types of Solar Panels
There are three main types of solar panels used in the UK:
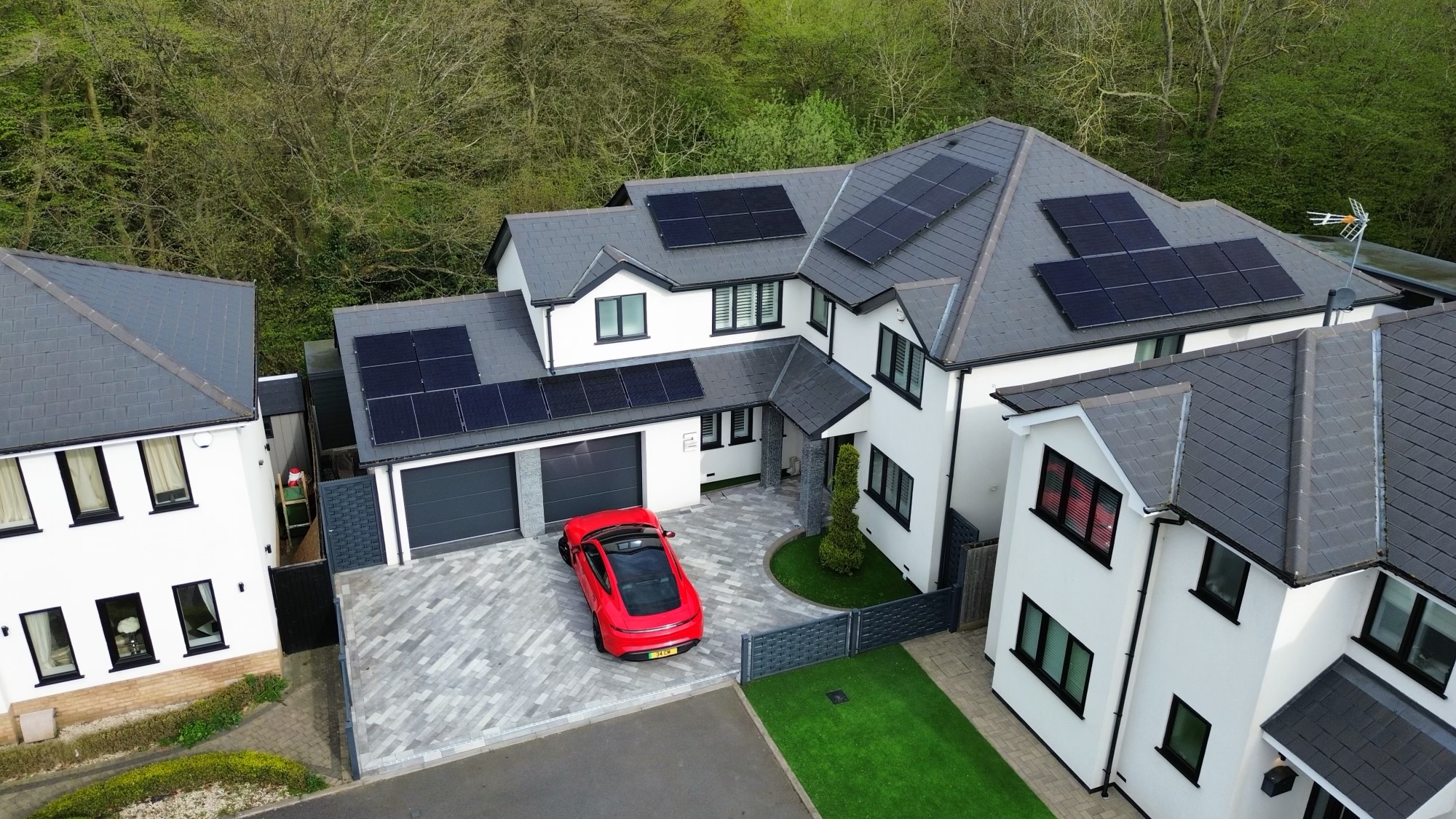
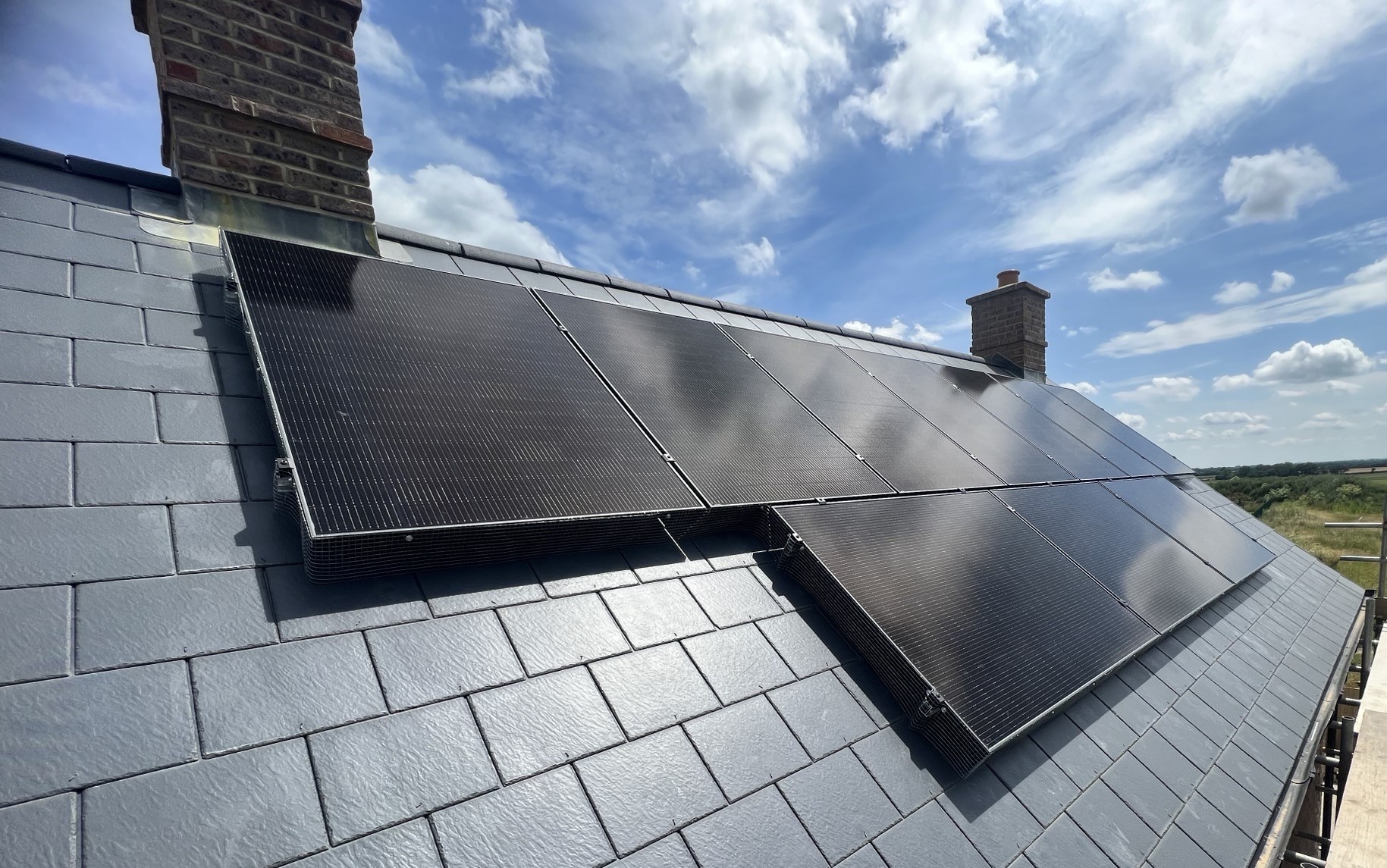
Monocrystalline Solar Panels
- Made from a single, high purity silicon crystal
- Highest efficiency and longest lifespan
- Perform better in low light conditions
- Typically black in appearance
Monocrystalline panels are what SolarTherm UK installs currently. They are best for homes with limited roof space or those seeking maximum output.
Polycrystalline Solar Panels
- Made from multiple silicon crystals
- Slightly lower in efficiency than monocrystalline panels
- Usually blue in colour
- More cost effective
Polycrystalline panels are better for properties with larger roof space who are looking to reduce upfront costs.
Thin Film Solar Panels
- Lightweight and flexible
- Lower efficiency and shorter lifespan
- Less common for residential installations
Thin film solar panels are used on specialist installations rather than standard UK rooftops.
What Affects Solar Panel Output?
Several key factors influence how much electricity a solar panel system can generate.
Efficiency
Panel efficiency refers to how much sunlight is converted into electricity. Higher efficiency panels produce more power from the same amount of roof space.
Orientation and Tilt
In the UK, solar panels perform best when facing south and installed at a tilt of 30-40 degrees. East- or west-facing roofs can still perform well, particularly when paired with battery storage.
Shading
Shading from trees, chimneys or nearby buildings can significantly reduce output. Even partial shading can affect performance, which is why professional system design is essential.